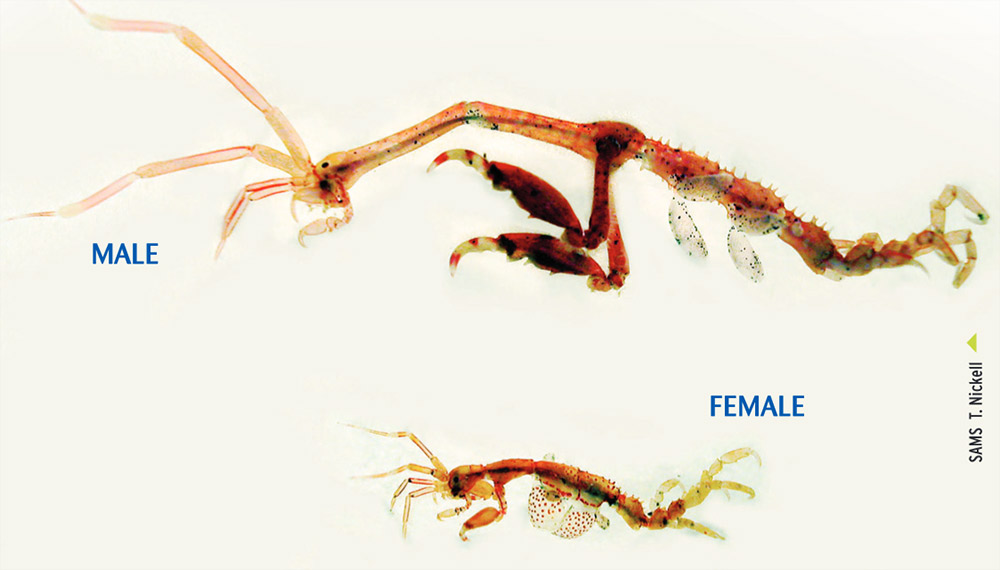
Japanese Skeleton Shrimp
Caprella mutica
Report it
If you think you have found an aquatic invasive species:
- take photos
- note:
- the exact location (GPS coordinates)
- the observation date
- identifying features
- contact us to report it
Identifying features
- Maximum size: males 3.5 cm and females 1.5 cm;
- Colour: variable from pale orange to red;
- Long cylindrical body, males with a long two-segmented neck;
- Females carry eggs in a ventral (belly) pouch, which is covered with dark red spots;
- Males very hairy on neck and claws.
Similar species (native)
There are several native caprellid species that resemble the Japanese Skeleton Shrimp. However, these species grow mainly on natural substrates and are not hairy.
Where it has been found
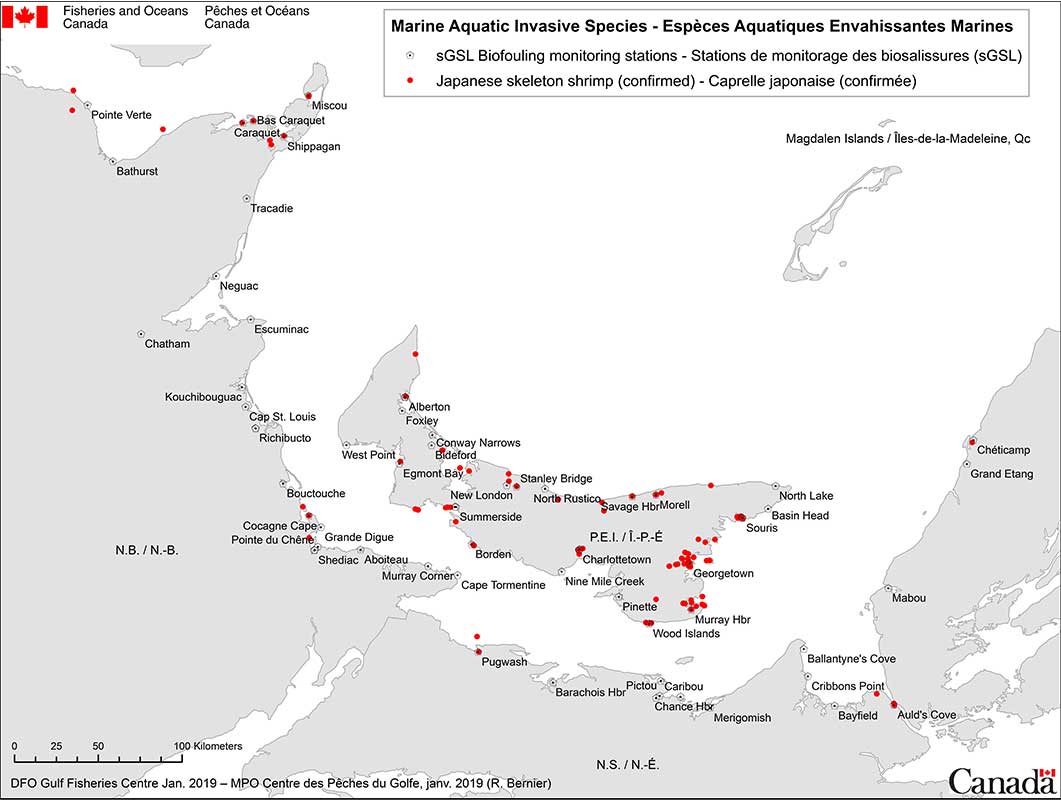
It was first reported in eastern Canada in the 1990's in the Bay of Fundy, and was then reported in Prince Edward Island in 1998, in Quebec in Chaleur Bay in 2003 and recently on the coasts of British Columbia. It is also present on the Gulf shore of Nova Scotia as well as the northeastern shore of New Brunswick.
Habitat
Common on man-made structures such as ropes, buoys, artificial reefs, breakwaters and mussel aquaculture socks. Often very abundant.
Like many invasive species Japanese Skeleton Shrimp reproduces rapidly, has a varied diet and tolerates a wide range of temperatures and salinities.
Ecological and economic impacts
Ecological threats
Despite the introduction of Japanese Skeleton Shrimp in several countries.
Few direct or indirect impacts have been observed fallowing the Japanese Skeleton Shrimp introduction in several countries. As this species abundance is higher during the summer, it would be more likely to observe its impact during this season.
Socioeconomic threats
Infests man-made structures such as buoys and mussel aquaculture socks, sometimes reaching numbers of 100,000 individuals per square meter. It may compete with mussels for food and space.
Origins and mode of arrival
Native from eastern Asia
The transport of organisms for aquaculture and by ballast waters are identified as the most plausible vectors of introduction in North America.
Government action
Scientific research
Fisheries and Oceans Canada is studying the Japanese Skeleton Shrimp population to improve its understanding of how it reacts and adapts to Canadian conditions and to follow the species distribution in St. Lawrence River.
Click image to enlarge.
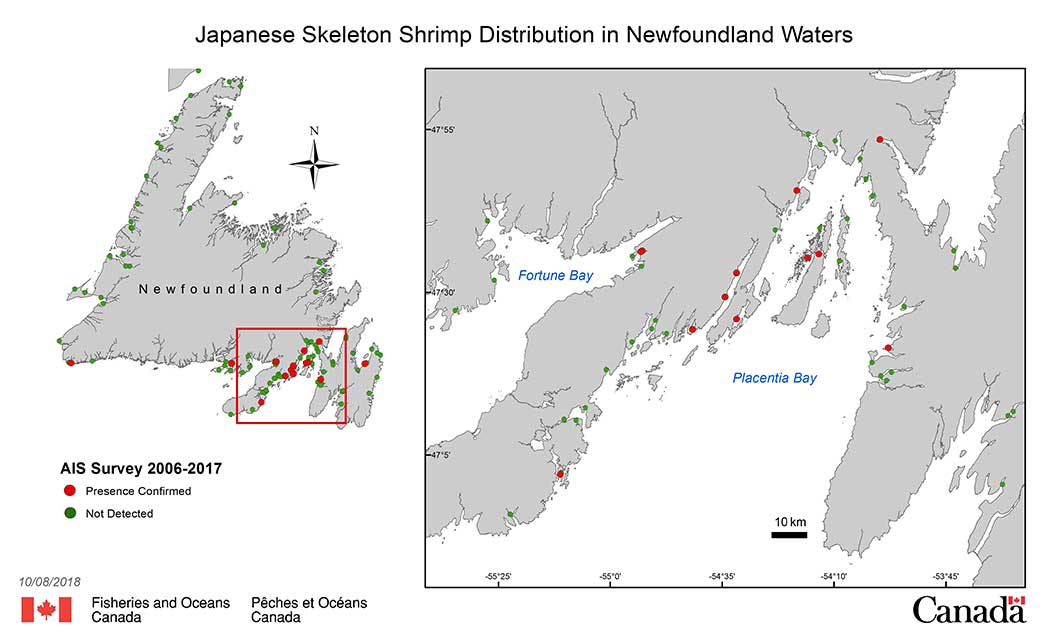
Distribution Location and Bay
- Bar Haven: Placentia Bay
- Bay East: Fortune Bay
- Big Southwest Cove: Placentia Bay
- Darbys Harbour: Placentia Bay
- Fox Harbour: Placentia Bay
- Foxtrap: Conception Bay
- Jean de Gaunt: Placentia Bay
- Marystown: Placentia Bay
- Paradise Sound: Placentia Bay
- Petite Forte: Placentia Bay
- Port aux Basques: Southwest Coast
- Presque Harbour: Placentia Bay
- Salmonier Cove: Connaigre Bay
- Sunnyside: Trinity Bay
For further information
- Canadian Science Advisory Secretariat (CSAS) Publications
- Identification Booklet of marine species in Eastern Canada
- Biological synopsis of the Japanese Skeleton Shrimp (Caprella mutica)
Fisheries and Oceans Canada -- 2009
References
- Turcotte, C. and B. Sainte-Marie. 2009. Biological synopsis of the Japanese skeleton shrimp (Caprella mutica). Can. Manuscr. Rep. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2903 : vii + 26 p.
- Date modified: